1 摘要
Despite the tremendous efforts by social media platforms and factcheck services for fake news detection, fake news and misinformation still spread wildly on social media platforms (e.g., Twitter). Consequently, fake news mitigation strategies are urgently needed. Most of the existing work on fake news mitigation focuses on the overall mitigation on a whole social network while ignoring developing concrete mitigation strategies to deter individual users from sharing fake news. In this paper, we propose a novel veracityaware and event-driven recommendation model to recommend personalised corrective true news to individual users for effectively debunking fake news. Our proposed model Rec4Mit (Recommendation for Mitigation) not only effectively captures a user’s current reading preference with a focus on which event, e.g., US election, from her/his recent reading history containing true and/or fake news, but also accurately predicts the veracity (true or fake) of candidate news. As a result, Rec4Mit can recommend the most suitable true news to best match the user’s preference as well as to mitigate fake news. In particular, for those users who have read fake news of a certain event, Rec4Mit is able to recommend the corresponding true news of the same event. Extensive experiments on real-world datasets show Rec4Mit significantly outperforms the state-of-theart news recommendation methods in terms of the capability to recommend personalized true news for fake news mitigation.
2 💡Note
2.1 论文试图解决什么问题?
Most of the existing work on fake news mitigation focuses on the overall mitigation on a whole social network while ignoring developing concrete mitigation strategies to deter individual users from sharing fake news.
2.2 这是否是一个新的问题?
No, fake news mitigation has been explored before.
2.3 这篇文章要验证一个什么科学假设?
By veracity-aware and event-driven personalized news recommendation, Rec4Mit can effectively and concretely mitigate fake news.
2.4 有哪些相关研究?如何归类?谁是这一课题在领域内值得关注的研究员?
2.4.1 Fake News Mitigation
Only focus on the mitigation on the whole network while ignoring the concrete mitigation on individual users.
- Independent cascade (IC) and linear threshold (LT) model based
approaches.
- taking users as nodes and each edge between a pair of users indicates the influence between them.
- Point process model based approaches.
- Reinforcement learning (RL) based approaches.
2.4.2 News Recommendation
- RNN, Attention, CNN, GNN, Knowledge distillation and RL: all of these methods are for conventional news recommendation and cannot be employed to fake news mitigation task which has unique data and goal.
- Recommender systems for mitigating fake news: fact-check URL
2.5 🔴论文中提到的解决方案之关键是什么?
2.5.1 Problem Formulation
User-news interaction: each user's sequence of historical interactions (e.g., clicks or reading) with news in a certain time period.
- News sequences interacted by all users:
: pieces of news which are sequentially interacted by a given user . : the whole news set.
records the meta information. - Context
: for each user , given the historical true and/or fake news pieces interacted by . - Goal:
- To learn the user's dynamic reading preference from
and predict the label (i.e., true or fake) of each piece of candidate news based on its meta information. - To generate a recommendation list of predicted true news which can best satisfy the user's reading preference at the moment.
- To learn the user's dynamic reading preference from
2.5.2 Methodology
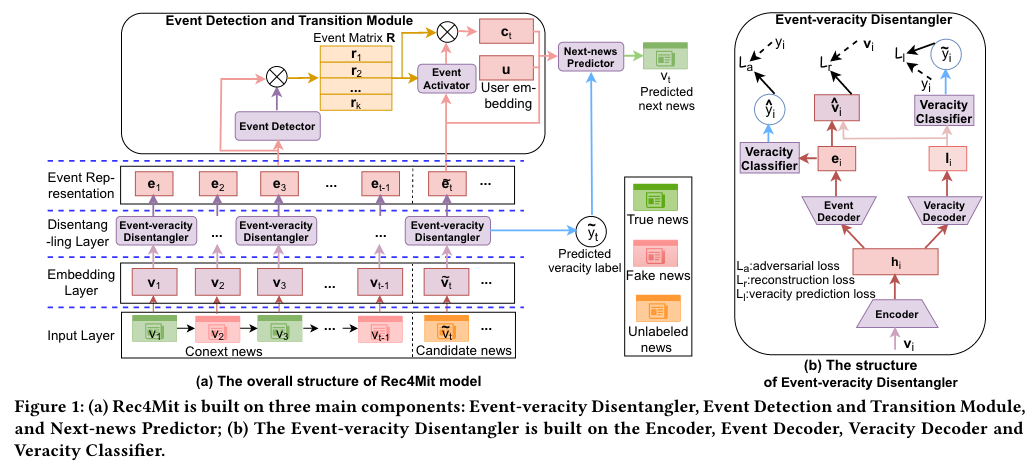
The overall structure of Rec 4 Mit model.
Input: a context consisting of a sequence ofinteracted news pieces.
Output: predicted next news.
2.5.2.1 Event-veracity Disentangler
How to model the transition over latent events while avoiding the interference from news veracity related information (e.g., news content style)?
- To avoid the interference between event information and label information of a piece of news.
- An adversarial auto-encoder framework
- Encoder: BERT + 3-layer MLP with LeakyReLU
- Input: a piece of news
. - Output: news embedding
. - Embedding of news ID
- Embedding of news meta information
: a concatenation of both news title embedding and news description embedding.
- Embedding of news ID
- Input: a piece of news
- Event decoder: 3-layer MLP with LeakyReLU and residual
connection
- Input: news abstract representation
- Output: latent representation
of events behind news
- Input: news abstract representation
- Veracity decoder: 3-layer MLP with LeakyReLU and residual
connection + news veracity classifier
- Input: latent representation of events behind news
- Output: the label representation
- Function:
- Forced to extract the veracity-specific information.
- Used to predict the label of each candidate news so that only true news would be recommended.
- Input: latent representation of events behind news
- Loss function module
- Reconstruction loss
- Label prediction loss:
- binary cross entropy
,
- binary cross entropy
- Adversarial loss:
- To ensure the disentangled event representation is pure and does not contain label-related information.
- The overall loss:
.
- Reconstruction loss
- Encoder: BERT + 3-layer MLP with LeakyReLU
2.5.2.2 Event Detection and Transition Module
To identify which event (s) the user is focusing on and how her/his reading preference regarding event is changing along with her/his reading history.
- Event detector: to detect the possible latent event (s)
associated with each news.
- Input: the event representation
of news - Arch:
- A softmax layer to obtain an event distribution vector to indicate
the possibility of
belonging to each of the latent events: , - Split the event representation
into event-specific representation vectors: .
- A softmax layer to obtain an event distribution vector to indicate
the possibility of
- Output:
event-specific representation vectors.
- Input: the event representation
- Event transition net: to model the complex transition
relations within and between events over a sequence of context news read
by a user.
- Event memory module
- To store the detected
event-specific representations for each piece of news in the context.
- Input: an event-specific representation tensor
- Arch: Attention-based aggregation
- Event representation
- Learnable position embedding
- the
-th row of matrix :
- Event representation
- Output: event-aware matrix
, where ..
- To store the detected
- Event activator
- To activate those events in the memory matrix which are closely related to the next target news.
- Input: the disentangled event representation
of is used as the activation signal. - Output: the user-aware and candidate news-specific context
embedding.
- The candidate news-specific context embedding:
- The activation degrees of all the
events behind :
- The candidate news-specific context embedding:
- Event memory module
2.5.2.3 Next-news Prediction Module
To predict the next news for user
- The total loss:
- The loss generated during the next-item prediction task
- Cross-entropy loss:
- A contrastive pair
from a news context - Taking the ground truth next news
as the positive sample and randomly sampling n pieces of news from the news set as the negative sample set .
- A contrastive pair
- Cross-entropy loss:
- The loss generated during the disentangling operation on context
news
- The loss generated during the disentangling operation on candidate
news
- The loss generated during the next-item prediction task
2.6 论文中的实验是如何设计的?
- Data preparation
- Extract the sequence of news (contain true and/or fake news) read by
each user on Twitter.
- News content
- Social context
- Spatiotemporal information
- Order these pieces of news by the reading timestamp to form a news sequence.
- All the sequences together form the user-news interaction dataset.
- the meta information including the title and one-paragaph description of each news is extracted to form the news information table. ## 2.7 用于定量评估的数据集是什么?评估标准是什么?Baseline是什么?
- Extract the sequence of news (contain true and/or fake news) read by
each user on Twitter.
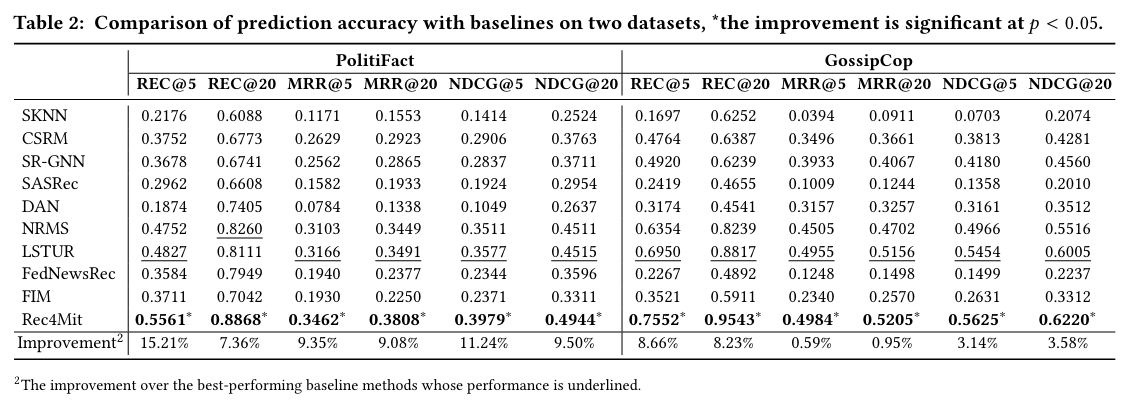
- 数据集: PolitiFact and GossipCop
- 指标:
- The prediction accuracy to measure whether an recommendation
approach can accurately recommend the right news to well match a user's
reading preference.
- Recall, mean reciprocal rank (MRR) and normalized discounted cumulative gain (NDCG)
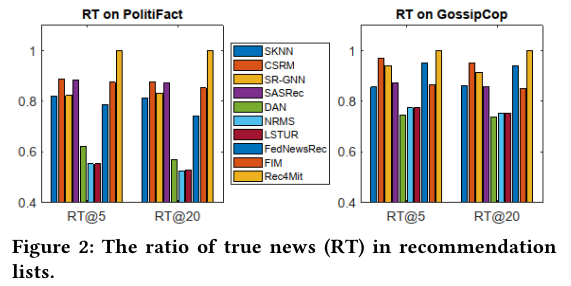
- The ratio of true news included in the recommendation list
.
- The prediction accuracy to measure whether an recommendation
approach can accurately recommend the right news to well match a user's
reading preference.
- 基线: sequential/session-based news recommendation baselines
2.8 论文中的实验及结果有没有很好地支持需要验证的科学假设?
实验结果:Comparisons w.r.t. Prediction Accuracy.
实验结果:Comparisons w.r.t. the Ratio of True News.
2.9 这篇论文到底有什么贡献?
- News recommendation to mitigate fake news.
2.10 下一步呢?有什么工作可以继续深入?
- Extend to graph learning.